10 Advantages of LEDs When Compared To Traditional Lighting

In this article, you will learn about 10 Advantages of LEDs when compared to Traditional Lighting. This means that LEDs are able to reliably and safely illuminate UV sensitive items like art that will break down and degrade over time if exposed to this type of emission.
Advantages of LED Lighting
1. LED Light Lifespan:
When compared to traditional lighting, the most significant advantage of LEDs is the long lifespan. An average LED lasts 50,000 to 100,000 operating hours or more.
That is 2-4 times as long as most metal halide, fluorescent, and even sodium vapor lights. Compared to the average incandescent bulb, it is more than 40 times as long.
Less frequent replacement means two major things: lower costs for replacement parts (because the bulbs simply do not fail for a long time) and lower maintenance costs in terms of labor.
2. LED Energy Efficiency:

LEDs usually consume very low amounts of power. The statistics to look for when comparing the energy efficiency of various lighting solutions are called by one of two terms: useful lumens or luminous efficacy.
These two things essentially describe the amount of light emitted per unit of power (i.e. Watts) consumed by the bulb. Depending on the existing lights and the specifically LEDs installed, the savings could be more than 90%.
3. Improved Safety With LEDs:

When it comes to LED lighting, safety is perhaps the most often overlooked advantage. The number one hazard or threat when it comes to lighting is the emission of heat.
Traditional bulbs such as incandescent convert more than 90% of the total energy used to power them directly into heat while the LEDs emit almost no forward heat.
This means only 10% of the total energy powering incandescent lights is actually used for light which also makes them extremely inefficient compared to LEDs.
Also as the LEDs consume less power they can operate effectively on low-voltage electrical systems. These are typically much safer in case something goes wrong.
4. LED Lights Are Physically Small:
The actual LED device is exceptionally small in size. Large power devices can be as small as an mm2 while a smaller power device is less than a tenth of a single mm2. Their small size makes LEDs incredibly versatile to an infinite number of lighting applications.
Different uses for LEDs include traffic signals to modern mood lighting, a wide spectrum from their roots in circuit board lighting and commercial and residential property applications, and even major stadium lighting.
5. LEDs Have Great (CRI) Color Rendering Index:
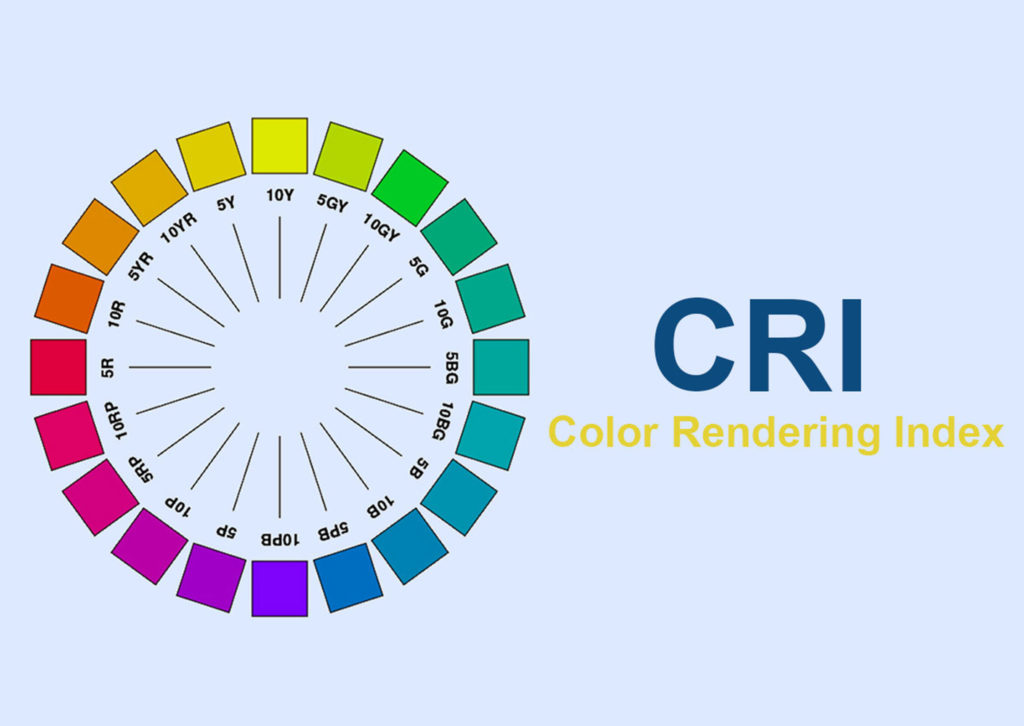
CRI or Color Rendering Index is a measurement of a light’s ability to reveal the actual color of objects as compared to an ideal light source (natural light). High CRI is usually a desirable characteristic.
6. LEDs typically have very high (good) ratings when it comes to CRI.
Perhaps the best way to appreciate CRI is to look at a direct comparison between a traditional lighting solution like sodium vapor lamps (which generally have poor CRI ratings and in some cases are almost monochromatic) and LED lighting (with a high CRI).
The range of possible values for different LED lights is typically between 65 and 95 which is considered excellent.
7. LEDs Generate Directional Emissions:
LED technology emits or releases light for only 180 degrees. Every other type of light emits or releases light 360 degrees around the source. 360-degree emissions necessitate or entail accessory devices to redirect and/or reflect the light.
This in general drives up the costs for the system and inevitably results in losses which means that the device is necessarily less efficient than it otherwise would be.
Think carefully about a light that emits light into the ceiling – that is your standard bulb. The problem or issue is that you’re trying to illuminate the room, not the ceiling. LEDs solve this issue completely and give the savings back in terms of the system’s overall energy efficiency.
8. LED Dimming Capability:
LEDs are able to work or operate virtually at any percentage of their rated power. Note that they require hardware specific to LED technology in order to dim (meaning you cannot use the dimming equipment for traditional lighting technology like an incandescent bulb).
A benefit or advantage of operating LEDs at less than full power is that they get more efficient as the power is reduced. Hence this increases the total lifespan of the light itself.
Both of those advantages or benefits are absent with technologies like metal halides that actually get less efficient at lower power and in many cases or situations cannot be dimmed at all.
9. LED Lights Are Environmentally Safe and Produce Zero UV Emissions:
LEDs do not have environmental issues common to traditional lighting solutions like mercury vapor lights or fluorescent.LEDs emit or release the vast majority of their energy in the visible spectrum, virtually none in the ultraviolet portion of the spectrum, and a small amount in the infrared spectrum.
10. LEDs Operate on Very Low Voltage and operate well In Cold and Hot Temperatures:
In many cases or situations, LEDs operate on very low voltages. This makes them suitable or apt for use in outdoor lighting applications where other lighting might not meet the requirement for e.g. with oceanfront homes where the properties ground level is in a flood zone.LEDs work well without significant degradation in a wide range of operating temperatures.


